Seja a circunferência dada pela equação . Se é o ponto em mais próximo da origem, então:
CossenoGPT
Teste
gratuitamente agora
mesmo! 

$• \ \text{Resolução I:}$
Segundo a equação do enunciado, podemos reduzi-la:
\begin{matrix} x^2 + 2x + \color{royalblue}{1} + y^2 + 6y + 9 = \color{royalblue}{1} &\Rightarrow& (x + 1)^2 + (y + 3)^2 = 1^2
\end{matrix} Assim, temos o raio $r = 1$ e, o centro $C = (-1,-3)$. Dessa forma, esboçando a situação num par de eixos coordenados não é difícil identificar a situação abaixo:
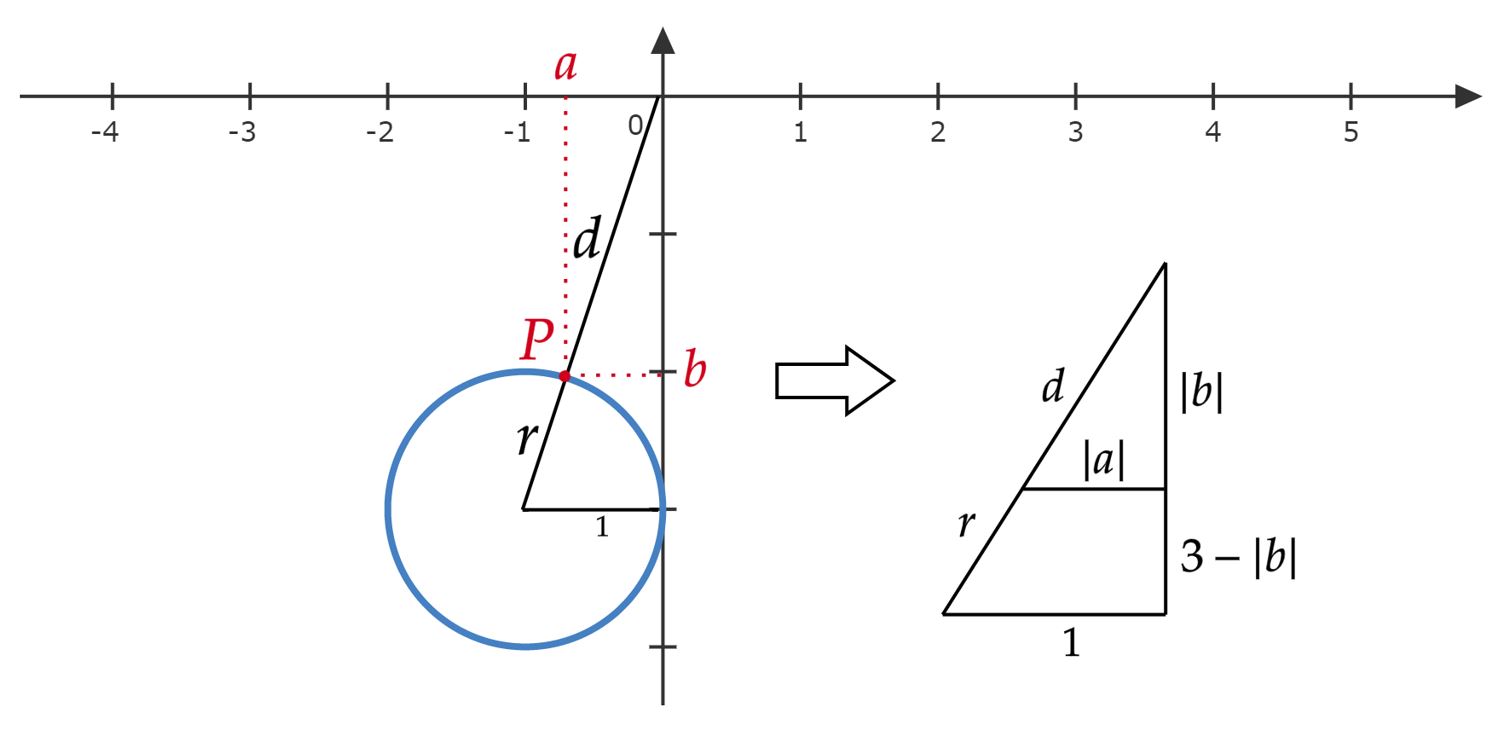 Aplicando Pitágoras não é difícil encontrar: \begin{matrix} (d+r)^2 = 10 &\Rightarrow& |d+r| = \sqrt{10} &,& |d| = \sqrt{10} - 1
\end{matrix}Atente a semelhança de triângulos, podemos fazer: \begin{matrix} \large{ \{ \frac{|b|}{|a|} = \frac{3}{1} } &,& \large{ \frac{|a|}{|d|} = \frac{1}{|d+r|} } \}&\Rightarrow&|b| = 3|a| &,& |a| = 1 - \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}
\end{matrix} Como $a,b <0$, concluímos: \begin{matrix} \fbox{$ \begin{matrix} b = 3a &,& a = \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10} - 1 \end{matrix} $}
\end{matrix}
$• \ \text{Resolução II:}$
Pensando um pouco diferente, poderíamos começar analisando a equação do enunciado a partir da equação geral de uma circunferência, dada como: \begin{matrix} x^2 + y^2 + 2hx + 2ky + h^2 + k^2 = r^2 &\Rightarrow& h = 1 \ , \ k = 3 \ , \ r = \sqrt{k^2 + h^2 - 9}
\end{matrix}Voltando na imagem, repare que podemos encontrar o coeficiente angular $(m)$ da reta fazendo:
\begin{matrix} m = \frac{0 - (-3)}{0 - (-1)} &\Rightarrow& m = 3
\end{matrix} Da origem ao ponto $P$, \begin{matrix} m = \large{ \frac{b-0}{a-0} }&\Rightarrow& \fbox{$b= 3a$}
\end{matrix} $\text{Distância Euclidiana} $ entre $P$ e $C$, \begin{matrix} r^2 = (a +1)^2 + (b + 3)^2 &\Rightarrow& (a+1)^2 = \large{\frac{1}{10}} &\Rightarrow& \fbox{$a = \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10} - 1$}
\end{matrix} \begin{matrix} Letra \ (C)
\end{matrix}
Aplicando Pitágoras não é difícil encontrar: \begin{matrix} (d+r)^2 = 10 &\Rightarrow& |d+r| = \sqrt{10} &,& |d| = \sqrt{10} - 1
\end{matrix}Atente a semelhança de triângulos, podemos fazer: \begin{matrix} \large{ \{ \frac{|b|}{|a|} = \frac{3}{1} } &,& \large{ \frac{|a|}{|d|} = \frac{1}{|d+r|} } \}&\Rightarrow&|b| = 3|a| &,& |a| = 1 - \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10}
\end{matrix} Como $a,b <0$, concluímos: \begin{matrix} \fbox{$ \begin{matrix} b = 3a &,& a = \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10} - 1 \end{matrix} $}
\end{matrix}
$• \ \text{Resolução II:}$
Pensando um pouco diferente, poderíamos começar analisando a equação do enunciado a partir da equação geral de uma circunferência, dada como: \begin{matrix} x^2 + y^2 + 2hx + 2ky + h^2 + k^2 = r^2 &\Rightarrow& h = 1 \ , \ k = 3 \ , \ r = \sqrt{k^2 + h^2 - 9}
\end{matrix}Voltando na imagem, repare que podemos encontrar o coeficiente angular $(m)$ da reta fazendo:
\begin{matrix} m = \frac{0 - (-3)}{0 - (-1)} &\Rightarrow& m = 3
\end{matrix} Da origem ao ponto $P$, \begin{matrix} m = \large{ \frac{b-0}{a-0} }&\Rightarrow& \fbox{$b= 3a$}
\end{matrix} $\text{Distância Euclidiana} $ entre $P$ e $C$, \begin{matrix} r^2 = (a +1)^2 + (b + 3)^2 &\Rightarrow& (a+1)^2 = \large{\frac{1}{10}} &\Rightarrow& \fbox{$a = \frac{\sqrt{10}}{10} - 1$}
\end{matrix} \begin{matrix} Letra \ (C)
\end{matrix}

Ampliar Imagem

